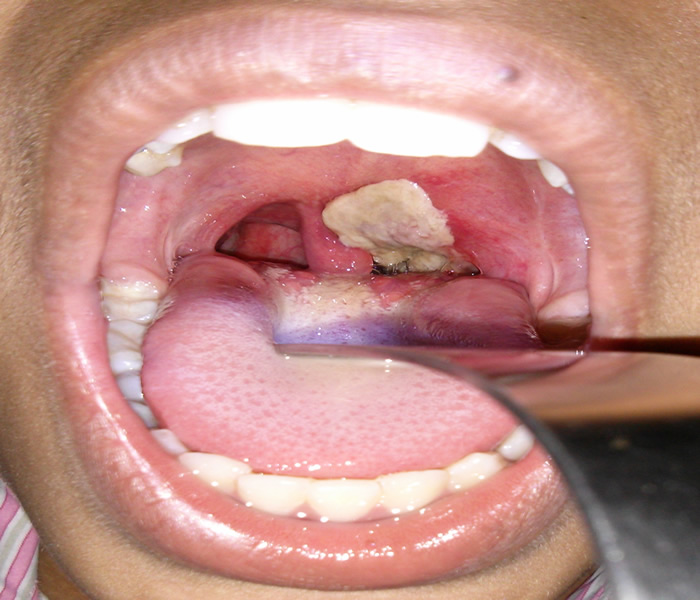
Nigeria is grappling with a significant diphtheria outbreak, having recorded 25,812 confirmed cases out of 42,642 suspected cases as of March 9, 2025. This data, spanning from week 19 of 2022 to week 10 of 2025, reveals a concerning spread of the disease across 36 states, the Federal Capital Territory, and 350 local government areas, with confirmed cases concentrated in 184 LGAs across 26 states. Tragically, the outbreak has claimed 1,319 lives, representing a case fatality rate of 5.1 percent. The data underscores the urgent need for intensified control and prevention measures to curb the further spread of this preventable disease and reduce its devastating impact on communities.
The geographical distribution of the outbreak reveals a heavy concentration of cases in a few states. Kano State bears the brunt of the outbreak, accounting for 18,108 confirmed cases, followed by Yobe with 2,408, Bauchi with 2,334, Katsina with 1,501, and Borno with 1,161 cases. These five states alone account for the vast majority of confirmed cases. Other states, while reporting lower numbers, still contribute to the overall burden of the disease. This uneven distribution highlights potential disparities in healthcare access, vaccination coverage, and public health infrastructure, which could be contributing to the localized intensity of the outbreak in these specific regions.
The age demographics of the affected population paint a stark picture of the vulnerability of children to diphtheria. A staggering 62.9 percent of confirmed cases, or 16,234 individuals, are children aged between one and 14 years. This statistic highlights a critical gap in vaccination coverage among this vulnerable age group. Furthermore, the data reveals that only 19.3 percent of confirmed cases were fully vaccinated against diphtheria, underscoring the urgent need for strengthening routine immunization programs and increasing vaccination coverage to protect children from this preventable disease. The high proportion of cases among children emphasizes the need for targeted interventions focused on improving childhood vaccination rates and ensuring equitable access to immunization services across the country.
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) is actively engaged in combating the outbreak, providing technical and on-site support to states across the country. These efforts include assistance with case identification, reporting, and response, particularly in states with low reporting rates or disease burden. The NCDC is also working to harmonize data from laboratories and case management teams to provide a comprehensive overview of the outbreak’s trajectory. However, the agency faces challenges such as low test positivity rates, inadequate reagents and consumables for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing directly on clinical samples, and the need for improved coordination and collaboration among various stakeholders.
Despite these challenges, the NCDC is committed to continuing its efforts to control the diphtheria outbreak. The agency’s ongoing activities include harmonizing case management data, following up with states, collecting data from treatment centers, providing on-site and remote support to affected areas, collaborating with partners, and supervising risk communication and community engagement (RCCE) activities at the state level. The NCDC is also leveraging social media platforms to raise awareness about diphtheria through comics and interviews with survivors. These multifaceted interventions aim to strengthen surveillance, improve case management, and enhance public awareness to control the spread of the disease.
Furthermore, the NCDC is pursuing crucial scientific endeavors to better understand and combat the outbreak. These include whole genomic sequencing of confirmed isolates to track the evolution of the diphtheria-causing bacteria and optimize PCR protocols for clinical samples. The agency is also working to enhance capacity building for laboratory diagnosis using PCR directly on clinical samples and provide support to testing sites by supplying reagents and consumables. These scientific initiatives are vital for improving diagnostic accuracy, monitoring the spread of different strains of the bacteria, and ultimately informing more effective control strategies. The NCDC’s concerted efforts, alongside collaboration with stakeholders, are critical for mitigating the impact of the diphtheria outbreak and protecting vulnerable populations.