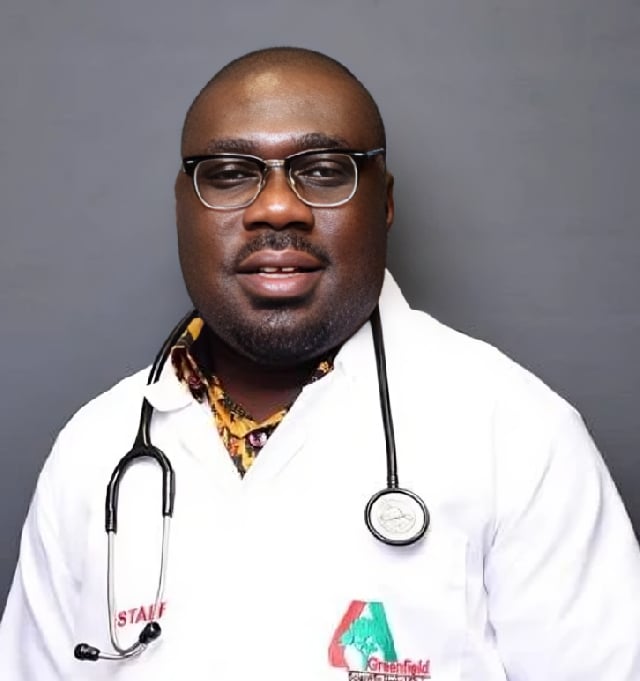
Dr. Bright Okoh, a renowned herbal medicine practitioner and founder of Greenfield Scientific Herbal Clinic in Nungua, Ghana, has issued a cautionary statement regarding excessive water consumption, linking it to potential kidney disorders. This warning emerged during a discussion on the “Journey to Heaven” drive-time program hosted by Taller Dee on No.1 105.3 FM. The conversation sparked when Dee revealed his own substantial water intake of 4,500ml that day, prompting Dr. Okoh’s concern. While acknowledging that Dee’s consumption wasn’t extreme, Dr. Okoh emphasized that significantly exceeding healthy water intake levels could strain kidney function.
The crux of Dr. Okoh’s argument lies in the kidneys’ crucial role in filtering and processing ingested fluids. The kidneys act as the body’s purification system, meticulously separating essential components from excess water, which is then expelled as urine. Overburdening this delicate filtration mechanism with excessive water intake can lead to stress and potential damage over time. Dr. Okoh highlighted the principle of moderation, stressing that excess in any form, even with substances as vital as water, can be detrimental to health. His warning underscores the importance of finding a balance between adequate hydration and avoiding the potential harms of overhydration.
Understanding the kidneys’ function provides further context to Dr. Okoh’s warning. These bean-shaped organs, located on either side of the spine, perform a multifaceted role in maintaining the body’s internal equilibrium. They filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood, regulate blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production. This complex process requires a delicate balance, and excessive water intake can disrupt this equilibrium, potentially leading to various health complications, including a condition known as hyponatremia, characterized by dangerously low sodium levels in the blood.
Hyponatremia, a direct consequence of excessive water intake, occurs when the kidneys are unable to excrete the surplus water efficiently. This leads to a dilution of electrolytes, particularly sodium, in the bloodstream. Sodium plays a vital role in regulating nerve and muscle function, and its depletion can have severe consequences, ranging from mild symptoms like nausea and headaches to more serious complications such as seizures, coma, and even death in extreme cases. Therefore, while adequate hydration is essential for overall health, it must be balanced with an awareness of the potential dangers of overhydration and its impact on electrolyte balance.
The symptoms of hyponatremia can be subtle and easily mistaken for other conditions, further emphasizing the importance of mindful water consumption. Early symptoms often include nausea, vomiting, headache, confusion, and fatigue. As the sodium levels continue to drop, more severe symptoms can manifest, such as muscle weakness, spasms, or cramps, seizures, loss of consciousness, and coma. These symptoms underscore the critical role of sodium in maintaining neurological and muscular function and the potential dangers of disrupting this balance through excessive water intake.
Dr. Okoh’s expertise stems from his extensive experience in the field of herbal medicine. With over two decades of practice, he has established himself as a leading figure in alternative medicine, particularly in Ghana. His Greenfield Scientific Herbal Clinic has garnered recognition for its innovative approach to healthcare, blending traditional herbal remedies with modern scientific principles. His cautionary advice regarding excessive water intake, therefore, carries significant weight, coming from a practitioner deeply invested in promoting holistic health and well-being. His warning serves as a valuable reminder that even seemingly harmless substances, when consumed in excess, can have unintended and potentially harmful consequences. It underscores the importance of a balanced approach to health, considering both the benefits and potential risks of all lifestyle choices, including hydration practices.