The Emergence and Spread of Mpox in Ghana: A Public Health Concern
Ghana is facing a growing public health challenge with the emergence of Mpox, a viral disease formerly known as monkeypox. The Ghana Health Service (GHS) has reported a surge in cases, raising concerns about the potential for a wider outbreak. As of the latest update, the country has recorded 45 confirmed cases, a significant increase from previous reports. Two individuals are currently hospitalized, highlighting the severity of the disease, though no fatalities have been reported to date. The GHS is actively monitoring the situation nationwide and has implemented emergency response protocols to contain the spread. These measures include enhanced surveillance across all 16 regions of the country and active contact tracing to identify and isolate potential cases.
Ghana’s Proactive Response and Containment Strategies
The GHS, in collaboration with the Ministry of Health, is taking decisive action to address the Mpox outbreak. The Service has expressed confidence in its capacity to manage the situation and prevent a larger-scale epidemic. This confidence stems from the existing infrastructure, expertise, and resources available for infectious disease control. Director-General of the GHS, Professor Samuel Kaba Akoriyea, has reiterated the health system’s preparedness to detect, manage, and control outbreaks. He underscored the importance of public awareness and urged citizens to remain calm while adhering to preventive measures. The GHS is emphasizing public education and community engagement to ensure widespread understanding of the disease and its transmission.
Public Health Recommendations and Preventive Measures
Public health messaging emphasizes the importance of individual responsibility in preventing the spread of Mpox. Citizens are advised to avoid close contact with individuals exhibiting symptoms suggestive of the disease. Prompt reporting of suspected cases to the nearest health facility is crucial for early detection and intervention. The GHS is also promoting basic hygiene practices, including regular handwashing and proper mask use, as essential preventive measures. These simple yet effective strategies can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Understanding Mpox: Transmission, Symptoms, and Prevention
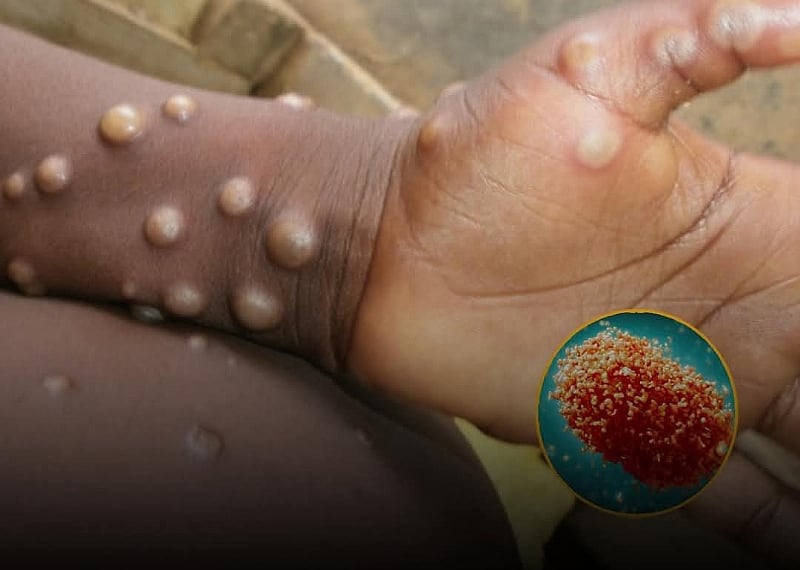
Mpox is a viral disease primarily transmitted through close contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated materials. The virus can enter the body through broken skin, the respiratory tract, or mucous membranes (eyes, nose, or mouth). Common symptoms of Mpox include fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, muscle aches, and back pain. The characteristic rash typically progresses through various stages, starting as flat lesions, then developing into raised bumps filled with clear fluid, followed by pus-filled bumps, and finally scabbing over. The rash can be itchy and painful, particularly during the pustular stage. To minimize the risk of transmission, the GHS recommends covering lesions when in the presence of others, avoiding shared personal items, disinfecting common areas, and using saltwater rinses for mouth sores.
Global Context and WHO Response to the Mpox Outbreak
The recent Mpox outbreak has garnered international attention, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare it a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in 2023. This designation reflects the rapid spread of a new variant across the African continent, where the majority of cases have been reported. According to the Africa CDC, over 17,000 suspected cases and 517 deaths were recorded in Africa last year, highlighting the significant impact of the outbreak. In response to the escalating situation, the WHO has approved the first Mpox vaccine, a crucial step in strengthening prevention efforts, particularly in Africa, where the outbreak has disproportionately affected communities. More than 20,000 people have been infected in the latest outbreak, underscoring the urgent need for effective control measures.
Continued Vigilance and Collaborative Efforts to Control the Outbreak
The Ghana Health Service remains committed to containing the Mpox outbreak and preventing further spread. Ongoing efforts focus on strengthening surveillance, enhancing public awareness, and promoting adherence to preventive measures. Public cooperation is essential in curbing the spread of the disease and protecting vulnerable populations. The collaborative efforts of the GHS, the Ministry of Health, and international partners, including the WHO, are instrumental in mitigating the impact of the Mpox outbreak and safeguarding public health in Ghana. Continued vigilance, proactive measures, and community engagement are critical to effectively managing this emerging health challenge.