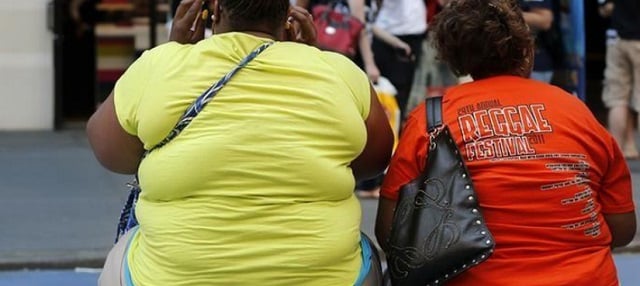Obesity is increasingly recognized as a significant public health issue in India, affecting various demographics, including men, women, and children. The ramifications of obesity extend beyond mere weight gain, presenting a range of symptoms including shortness of breath, fatigue, excessive sweating, and issues with physical exertion. Additionally, psychological ramifications such as depression are prevalent. The Body Mass Index (BMI) serves as a key metric, and its classifications range from overweight at a BMI of 25-29.9 to extreme obesity at a BMI over 40. Recent data from the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) highlights a disturbing trend: rates of overweight and obesity in women aged 15-49 have increased from 12.6% to 24% over the past 15 years, while rates for men in the same age group surged from 9.3% to 22.9%. Alarmingly, the prevalence of overweight children has dramatically increased, with figures reaching 12.5 million between the ages of 5 to 19 in 2022, compared to just 0.4 million in 1990.
The causes of obesity are multifaceted, involving genetic, lifestyle, cultural, and hormonal factors. Genetic predisposition profoundly influences how one’s body stores fat and metabolizes food. Sedentary lifestyles, exacerbated by urbanization and passive employment, have resulted in reduced physical activity and disrupted sleep patterns. Changing dietary habits, characterized by a significant increase in the consumption of processed and calorie-dense foods, have further compounded the issue. Cultural shifts, where convenience often supersedes nutritional value, and hormonal disorders like PCOS and hypothyroidism also contribute notably to the difficulty of maintaining a healthy weight. With 12.5 million overweight children, the urgency of addressing obesity in the younger population is critical.
The health risks associated with obesity are severe and can be life-threatening. Individuals who suffer from obesity are at a greater risk of developing various physical deformities and chronic diseases. Cardiovascular disease is notably linked to obesity, increasing the risk of stroke and heart disease. Furthermore, type 2 diabetes can result from excessive body fat, particularly around the waist, leading to insulin resistance. Joint problems, particularly osteoarthritis, can emerge due to the stress placed on joints by excess weight. Additional dangers include an increased risk of certain cancers, such as liver, colon, and breast cancer, as well as mental health issues stemming from societal stigma, contributing to anxiety and depression. Respiratory complications, such as sleep apnea, are also prevalent in individuals with obesity, further complicating their health status.
Though weight loss is achievable through various methods, it often involves confronting numerous side effects associated with anti-obesity medications, including vomiting, fatigue, and gastrointestinal disorders. To mitigate these effects and improve treatment efficacy, it’s crucial for patients to engage with healthcare specialists regularly to tailor their treatment plans. A diet rich in minerals and fibers, combined with consistent physical activity, is essential in supporting weight loss efforts and minimizing associated discomforts. Moreover, adequate hydration and sufficient sleep are critical components not only for losing weight but also for overall health improvement.
Addressing obesity necessitates a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and community support. Lifestyle changes should emphasize healthier dietary practices, increased physical activity, and behavioral therapy as primary strategies for weight loss. Several FDA-approved medications can assist in weight loss by either blocking fat absorption or suppressing appetite, while bariatric surgery remains an option for individuals with severe obesity who have not found success with non-surgical methods. New hormonal medications targeting metabolic pathways and appetite regulation have emerged, further diversifying treatment options. Support programs, particularly counseling and community-based initiatives, play a crucial role in promoting education and sustained weight loss efforts, ensuring that individuals have resources available to aid their journey.
Ultimately, combating obesity requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses community support, medical interventions, and individualized lifestyle changes. By addressing the underlying causes of obesity and implementing effective treatment options, significant strides can be made toward improving public health outcomes and mitigating the impact of this critical issue. Through concerted efforts from healthcare providers, individuals, and society at large, it is possible to foster a healthier environment and encourage sustainable habits that contribute to long-term health and well-being, ultimately lessening the burden of obesity in both India and globally.