Resurgence of Mpox: A Comprehensive Overview and Public Health Advisory
The global health landscape is once again facing the resurgence of Mpox, a viral zoonotic disease that poses a significant threat to public health. Characterized by its distinctive rash and flu-like symptoms, Mpox has re-emerged as a concern, prompting renewed vigilance and preventive measures. This comprehensive overview delves into the current epidemiological situation, transmission dynamics, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, treatment strategies, and preventive measures to provide a holistic understanding of the disease and empower individuals and communities to effectively combat its spread.
Epidemiological Update: A Growing Concern
Recent reports from health authorities indicate a disconcerting rise in Mpox infections globally. The Ghana Health Service (GHS), for instance, has confirmed a surge in cases, with nine new infections reported as of June 18, 2024, bringing the national total to 107. While no fatalities or hospitalizations have been recorded, the upward trend necessitates heightened awareness and proactive measures to mitigate further transmission. Contact tracing efforts are underway to identify and monitor potential exposures, and health surveillance has been intensified across various regions to detect and manage cases promptly. The projected increase in case numbers underscores the importance of sustained public health interventions.
Transmission Dynamics: Understanding the Spread
Mpox primarily spreads through close contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated materials. Direct contact with bodily fluids, lesions, or respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face interaction are common modes of transmission. Contact with contaminated objects, such as bedding, clothing, or surfaces, can also facilitate the spread of the virus. While less common, transmission can occur through respiratory droplets during close contact with an infected person exhibiting respiratory symptoms. Understanding these transmission pathways is crucial for implementing effective preventive strategies.
Clinical Manifestations: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
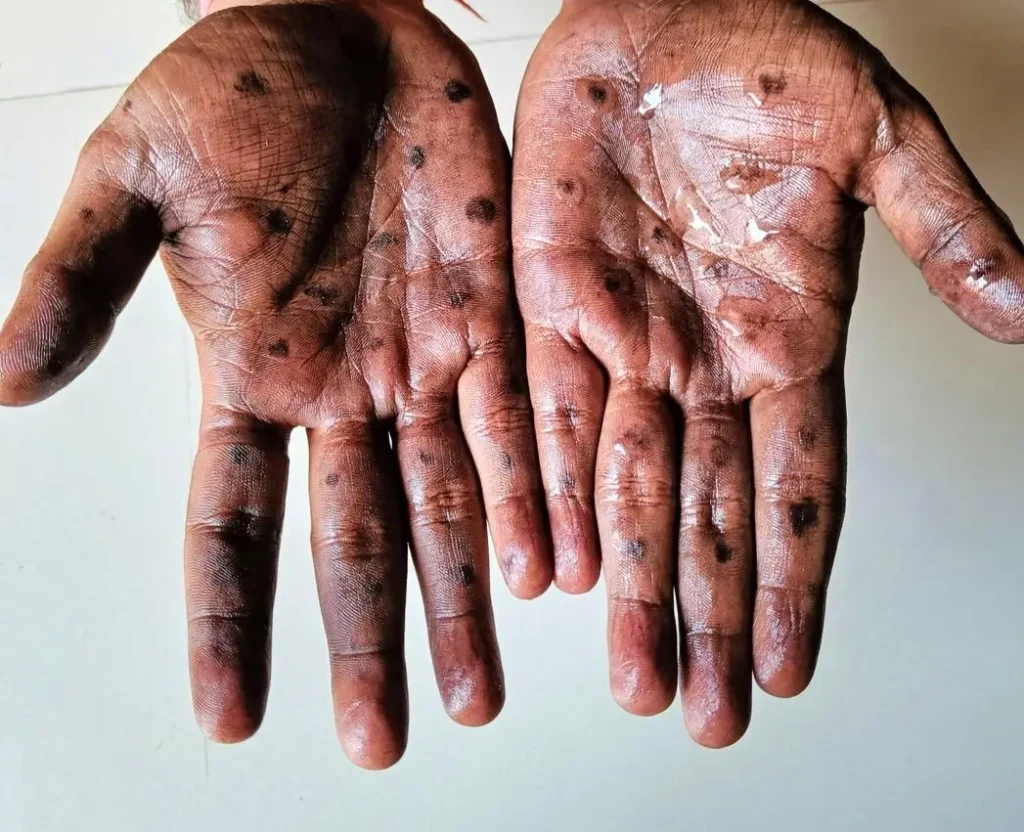
The clinical presentation of Mpox typically begins with flu-like symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, and fatigue. Swollen lymph nodes, a distinguishing feature of Mpox, often accompany these initial symptoms. Subsequently, a characteristic rash develops, progressing through various stages, from macules (flat lesions) and papules (raised lesions) to vesicles (fluid-filled lesions) and pustules (pus-filled lesions). The rash eventually scabs over and heals. The rash can appear on any part of the body, including the face, palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and genitals. The duration of symptoms typically ranges from two to four weeks.
Diagnostic Approaches: Early Detection is Key
Early diagnosis of Mpox is paramount for effective disease management and preventing further transmission. Laboratory testing is essential for confirming the diagnosis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of lesion swabs or biopsies is the most reliable method for detecting the Mpox virus. Other diagnostic techniques, such as serology and viral culture, may also be employed. Prompt diagnosis allows for timely implementation of infection control measures and appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment Modalities: Supportive Care and Antivirals
While there is no specific antiviral treatment approved for Mpox, supportive care is essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications. Adequate hydration, pain management, and wound care are crucial aspects of supportive care. In severe cases, antiviral medications, such as tecovirimat, may be considered. Furthermore, individuals diagnosed with Mpox should isolate themselves to prevent further spread of the virus. Close contacts of infected individuals should be monitored for symptoms and offered vaccination if eligible.
Preventive Measures: Protecting Yourself and Others
Prevention is the cornerstone of Mpox control. Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, is essential. Avoiding contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated materials is crucial. Vaccination is a highly effective preventive measure, especially for those at high risk of exposure, such as healthcare workers and close contacts of infected individuals. Raising public awareness about Mpox transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for empowering individuals and communities to protect themselves and others.
Public Health Implications and Future Directions
The resurgence of Mpox underscores the importance of robust public health infrastructure, surveillance systems, and preparedness measures. Continued research is needed to enhance our understanding of the virus, develop effective diagnostics and treatments, and refine preventive strategies. International collaboration and information sharing are crucial for coordinating global efforts to combat Mpox and prevent future outbreaks.
In conclusion, the resurgence of Mpox demands a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. By understanding the disease’s transmission dynamics, clinical manifestations, diagnostic approaches, treatment modalities, and preventive measures, we can effectively combat its spread and safeguard public health. Early diagnosis, prompt treatment, and adherence to preventive measures are essential for mitigating the impact of Mpox and protecting vulnerable populations.