Hemorrhoids, or piles, are a common ailment characterized by swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. These swollen veins cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms, including itching, pain, and sometimes bleeding. Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, including chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, straining during bowel movements, obesity, pregnancy, and a diet low in fiber. While these factors are well-established, some individuals have reported a curious phenomenon: their hemorrhoids seem to shrink immediately after sexual activity and ejaculation. This observation has led to investigations into the physiological mechanisms that might explain this temporary relief.
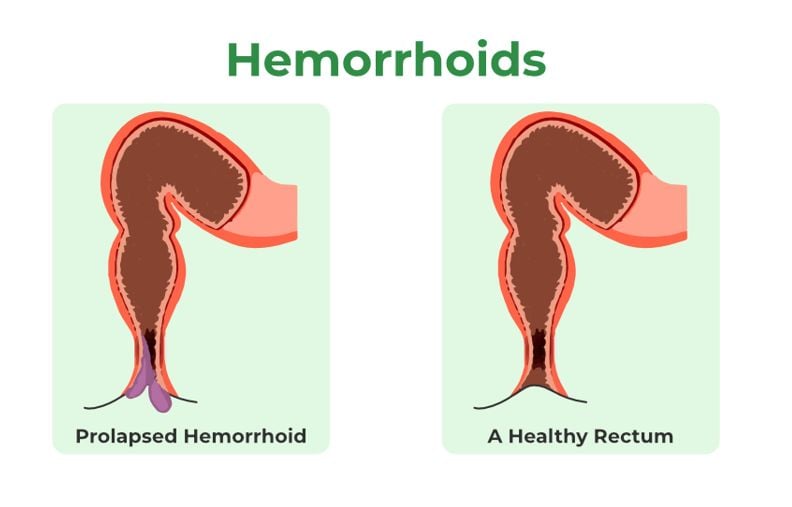
Understanding the underlying causes of hemorrhoids is crucial to exploring this phenomenon. Hemorrhoids form when increased pressure causes the veins in the lower rectum to swell. This pressure can result from straining during bowel movements, prolonged sitting, obesity, chronic constipation or diarrhea, pregnancy, and a low-fiber diet. Hemorrhoids are categorized as internal or external. Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are typically painless but can bleed. External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, form under the skin around the anus and are often painful and itchy.
The connection between sexual activity and hemorrhoid shrinkage likely involves several interconnected physiological processes. One primary factor is blood circulation. Poor blood circulation in the rectal veins contributes significantly to hemorrhoidal swelling. During sexual arousal and orgasm, blood flow is redirected to other areas of the body, such as the genitals, brain, and muscles. This redistribution can temporarily alleviate congestion in the rectal veins, leading to a decrease in hemorrhoid size. The increased heart rate and improved overall circulation during sexual activity can further contribute to clearing excess blood pooled in these veins.
Hormonal changes also play a role in this phenomenon. Sexual activity and orgasm trigger the release of hormones like oxytocin and endorphins. Oxytocin, known as the “love hormone,” has vasodilatory properties, meaning it widens blood vessels. This improved blood flow can help reduce vascular congestion, including in the rectal veins. Endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, potentially alleviating the discomfort associated with hemorrhoids. Furthermore, the release of dopamine and serotonin after ejaculation contributes to relaxation and stress reduction, indirectly aiding in hemorrhoid shrinkage.
The mechanics of ejaculation itself may also contribute to temporary hemorrhoid relief. Ejaculation involves rhythmic contractions of the pelvic floor muscles. These contractions can improve blood flow and reduce pressure in the rectal veins, leading to a temporary decrease in hemorrhoid size. The physical activity associated with sex also engages the lower abdominal muscles, further promoting better circulation in the pelvic region. Additionally, ejaculation may act as a short-term venous decongestant. The rapid fluid expulsion and muscle contractions could create a temporary shift in venous pressure, reducing swelling in the rectal veins.
Chronic stress can exacerbate hemorrhoid symptoms by increasing muscle tightness, inflammation, and digestive issues. Sex and orgasm, however, induce a state of relaxation, lowering stress hormones like cortisol. This stress reduction can improve digestive health, leading to softer stools and less straining during bowel movements, which ultimately benefits hemorrhoidal health. While the combination of these physiological effects can provide temporary relief, it’s important to remember that they do not address the underlying causes of hemorrhoids. The relief is transient, and the swelling will likely return if the contributing factors, such as poor diet or prolonged sitting, persist.
Therefore, long-term management of hemorrhoids requires a comprehensive approach that addresses these underlying causes. Increasing fiber intake is crucial, as a high-fiber diet promotes soft stools and prevents constipation, reducing strain during bowel movements. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water also helps maintain soft stools. Avoiding prolonged sitting, especially on hard surfaces, is essential to reduce pressure on the rectal veins. Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, improves circulation and prevents excessive pressure in the rectal area.
Practicing proper toilet habits is also important. Avoid straining during bowel movements and prolonged sitting on the toilet. Using a stool or adopting a squat position can facilitate easier bowel movements. Topical treatments, such as witch hazel, aloe vera, and coconut oil, can soothe inflamed hemorrhoids. Over-the-counter creams containing hydrocortisone may also provide relief. In severe or persistent cases, medical interventions like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or hemorrhoidectomy may be necessary. While the temporary relief experienced after sex can be a welcome respite, it’s essential to adopt a holistic, long-term strategy that addresses the root causes of hemorrhoids and promotes overall rectal health. Consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended for persistent or severe symptoms to explore the most appropriate treatment options.