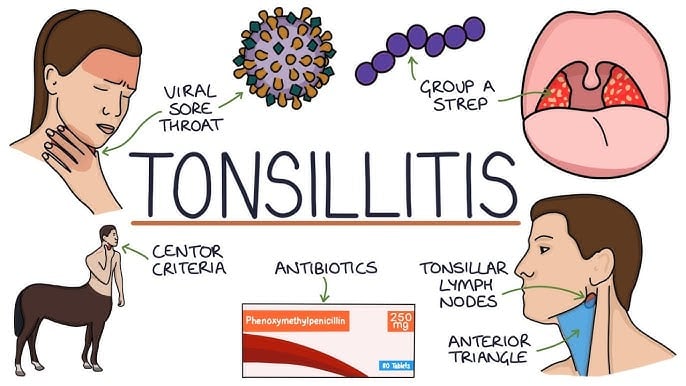
Tonsillitis, the inflammation of the tonsils, is a prevalent ailment affecting individuals across all age groups. Located at the rear of the throat, the tonsils play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, serving as the first line of defense against invading pathogens. Their constant exposure to infectious agents, however, makes them susceptible to inflammation, resulting in tonsillitis. The severity of tonsillitis varies widely, ranging from mild discomfort to excruciating pain, significantly impacting daily activities such as speech, swallowing, and even sleep.
This inflammation can stem from several factors, primarily viral and bacterial infections. Viruses like adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, and the influenza virus are common culprits, often associated with upper respiratory tract infections. Bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (strep throat), are another significant contributor. Beyond infections, environmental irritants such as dust, mold, and smoke can also trigger tonsil inflammation, leading to tonsillitis. Seasonal variations also play a role, with increased incidence during winter months when respiratory infections are more prevalent, often exacerbated by dry air and crowded indoor environments. A weakened immune system further increases susceptibility to tonsillitis.
The clinical presentation of tonsillitis spans a spectrum of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain. Red, inflamed tonsils are a hallmark sign, often accompanied by white or yellow patches. A sore throat and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) are common complaints. Systemic symptoms like fever, body aches, and fatigue may also manifest. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are frequently observed. In severe cases, bad breath and dehydration can occur.
Diagnosing tonsillitis involves a thorough clinical examination by a healthcare professional. Visual inspection of the throat often reveals the characteristic redness and swelling of the tonsils. A throat swab test is typically performed to determine the presence of a bacterial infection, particularly strep throat. This test involves gently swabbing the back of the throat to collect a sample for analysis. In some cases, blood tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions like mononucleosis.
Treatment strategies for tonsillitis are tailored to the underlying cause. For viral tonsillitis, the focus is on supportive care. Rest, adequate hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers are recommended to manage symptoms. Home remedies like gargling with salt water can provide some relief. Bacterial tonsillitis, on the other hand, requires antibiotic therapy to eradicate the infection. A complete course of antibiotics is crucial to prevent complications and recurrence. In cases of chronic or recurrent tonsillitis, where frequent episodes significantly impact quality of life, surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) may be considered. This procedure is typically reserved for patients who experience multiple bouts of tonsillitis within a specified timeframe.
Consultation with an ENT specialist is particularly important if complications arise. These may include the development of a peritonsillar abscess (a collection of pus behind the tonsils), difficulty breathing due to airway obstruction, or severe dehydration. An ENT specialist can provide expert evaluation, recommend appropriate treatment plans, and manage any complications effectively. They can also offer personalized advice on preventive measures to reduce the risk of future episodes.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for managing tonsillitis effectively. Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infections. Avoiding close contact with individuals exhibiting symptoms of respiratory infections is also advisable. Maintaining a healthy diet and ensuring adequate hydration contribute to a robust immune system, reducing susceptibility to infections. By adopting these preventive measures and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can minimize the impact of tonsillitis and maintain optimal health. Consulting with an ENT specialist can provide tailored guidance on prevention and management strategies, contributing to improved overall well-being.