Ghana’s Escalating Mpox Outbreak: A Growing Public Health Concern
Ghana is grappling with a burgeoning mpox outbreak, with the Ghana Health Service (GHS) reporting a concerning rise in cases. As of the latest update, the cumulative number of confirmed infections stands at 519, a figure that has steadily climbed in recent weeks. This escalating trend underscores the urgent need for heightened public awareness, strengthened surveillance measures, and robust public health interventions to curb further spread. The recent surge in cases, with 25 new infections reported, adds to the mounting concern. This follows a pattern of increasing numbers, with 27 cases reported on September 1st, 21 on August 28th, and 22 on August 25th, illustrating the accelerating transmission rate. This upward trajectory highlights the challenges in containing the outbreak and emphasizes the need for rapid and effective response strategies.
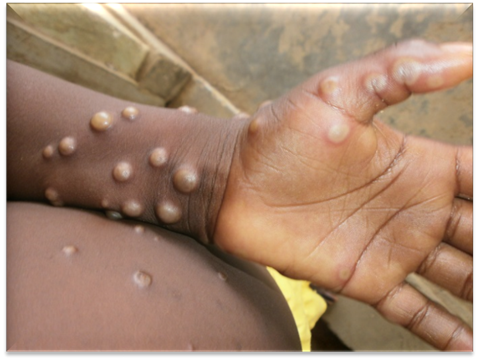
Mpox, a zoonotic disease caused by the mpox virus, poses a significant threat to public health. While typically less severe than smallpox, it can still manifest with a range of debilitating symptoms. The infection is characterized by an initial phase of flu-like illness, including fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, and swollen lymph nodes. This is followed by the development of a distinctive rash that progresses through various stages, from macules (flat lesions) to papules (raised lesions), vesicles (fluid-filled lesions), pustules (pus-filled lesions), and finally, scabs. The rash can be extremely itchy and painful, significantly impacting the patient’s quality of life. While the majority of cases resolve within a few weeks, severe complications, including secondary bacterial infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis, can occur, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
The primary mode of mpox transmission is through close physical contact with an infected individual. This can occur through direct contact with the characteristic rash, bodily fluids, or respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face interactions. Contact with contaminated materials, such as clothing, bedding, or towels used by an infected person, can also transmit the virus. While less common, transmission from animals to humans is possible through bites or scratches from infected animals, or through contact with their bodily fluids or contaminated materials. Understanding the various transmission routes is crucial for implementing effective preventative measures.
The Ghana Health Service (GHS) has issued a strong advisory, urging the public to remain vigilant and adopt preventive measures to mitigate the risk of infection. Maintaining good hygiene practices, including frequent handwashing with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, is paramount. Avoiding close contact with individuals exhibiting mpox symptoms, such as the distinctive rash, is crucial. This includes refraining from sharing personal items like clothing, bedding, and towels. Furthermore, practicing safe sex, including the use of barrier methods, can help reduce the risk of sexual transmission. The GHS has also emphasized the importance of seeking immediate medical attention if any mpox symptoms develop. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes and help prevent further spread of the disease.
The ongoing mpox outbreak in Ghana necessitates a comprehensive and multi-pronged approach. Strengthening surveillance efforts to promptly identify and isolate cases is critical. This involves enhanced contact tracing to identify individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, enabling timely intervention and preventing further transmission chains. Public health education campaigns play a vital role in raising awareness about mpox, its symptoms, transmission routes, and preventive measures. These campaigns should target diverse communities, utilizing accessible and culturally appropriate messaging to ensure wide reach and understanding. Collaboration with community leaders and healthcare providers can further amplify these efforts.
Ensuring access to appropriate medical care for individuals infected with mpox is paramount. This includes providing supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications. In cases of severe illness, antiviral medications may be considered. Healthcare workers should be equipped with the necessary knowledge and resources to diagnose and manage mpox cases effectively. Furthermore, research and development efforts should be prioritized to develop more effective diagnostic tools, treatments, and vaccines for mpox. International collaboration and information sharing are crucial to coordinate global responses and prevent the further spread of this emerging infectious disease. The collective efforts of governments, public health agencies, healthcare providers, and communities are essential to combat the growing threat of mpox in Ghana and safeguard public health.